Vocabulary and terms are not always understood in the same way. Also, each individual has his/her/their vision of trans-identity. Some may want to go under medical treatment and surgeries. Some don’t. Surgical techniques have improved a lot in the past decades to offer a wide range of possibilities to these people who feel the need and desire to undergo surgery to be truly themselves. Some people identify as non-binary gender. Here, we will mention those people who are on the path of transition towards their gender. FTM (Female to Male – born and recognized as female at birth but who doesn’t identify as such and identifies more as male) people may have several steps to complete for their transition. Each country also has its regulations and laws according to some steps (medication, psychological follow-up, surgeries etc.) One of the first medical steps consists in taking testosterone, allowing a better balance of hormones and several changes in the body. It increases libido and changes the whole metabolism and physical attributes (secondary sex-characteristics). Surgical steps are various and can depend from one person to another one. Phalloplasty is one of the last surgeries. It is the creation of a neo-phallus made of skin graft from another part of the body (forearm, leg, back, abdominal skin etc.) Despite their efforts to give the appearance and sensitivity of a penis, phalloplasty doesn’t include a glans formed of spongy tissues nor erectile corpora cavernosa anchored securely to the base of the pubis – that are both essential for achieving erections. A penile implant should be used for this purpose. Until 2016, devices used to provide erections in phalloplasty were the same devices used for cismen with erectile dysfunction. Surgeons had stretched their creativity trying to adapt these penile implants but many problems arose. In 2016, Zephyr Surgical Implants was aware that these devices were not perfectly fitting for transgender morphologies and phalloplasty. The company developed implants fitting more the requirements and constraints given by phalloplasty. Here, we explain each specificity that has been adapted. The ED penile implants were conceived solely for cismen. There are various categories—malleable implants and inflatable implants of two or three components (see figures)—but they were all designed to be inserted in the corpora cavernosa of the penis. This penile implant compensates for the erectile dysfunction of the corpora cavernosa, taking advantage of its firm attachment to the pubic base. Men with erectile dysfunction requiring this kind of device are generally over 50-60 years old, and passed through some medical issues (prostate cancer, surgery, radiotherapy etc.) that lead to ED. Natural glans is encapsulating the cavernous bodies, allowing sensations to be preserved and the tip of the cavernous bodies to be protected. Patient and/or partner don’t feel the ‘pointy’ device inserted. **We will use the terms FTM devices and ED devices to compare both types of devices. The ZSI 100 FTM and ZSI 475 FTM implants were designed to be inserted into a phalloplasty. They have been adapted to the specificities presented by the phalloplasty and the transmen morphology. A phalloplasty is a neo-penis made of skin graft. It has no inner structure such as cavernous bodies nor glans. The ED penile implant is composed of two elongated tubes more or less conical at their ends for insertion into the corpora cavernosa. They have a diameter between 13 mm and 14 mm. Their framework is not suited for transmen. There are several risks: To compensate the lack of inner structure of the phalloplasty, both inflatable and malleable FTM implants have the shape of a penis. They provide a framework that gives “structure” to the phalloplasty, without which the implant would be a graft of inert skin. Cavernous bodies allow penile implant to be fixed inside the penis. Since there are no cavernous bodies in the phalloplasty, the implant must be fixed to the pubis bone in order to achieve a stable and effective erection. ED penile implants present a problem in attaching to the pubis, because they were designed to be inserted into the cavernous bodies, allowing the cylinders to be well anchored. The ED penile implant does not include any element that can be attached to the pubis. Implants for phalloplasty have a fixation plate to be attached securely to the pubic bone using sutures or screws. This plate is rigid and perforated, but also malleable in order to adapt to the curved shape of the pubic bone. Cavernous bodies provide natural erection angle. Without them, if we implant an ED device onto the pubic bone, it will be pressed against the pubis without any angle of compensation. During penetration, this generates significant tensions in the implant, which may induce its “exit” from the Dacron pouch or the total separation of the apparatus. The FTM penile implant is not aligned with the pubic symphysis (the medial point where the two pubic bones join). There is an angle between the attachment plate at the pubis and the implant in erection. This angle reproduces the natural angle of the penis’s suspensory ligament. It is adapted for penetration and reduces tension in the penis and thus in the implant. ED penile implants are not designed to fold when deflated. When deflated, the silicone part affixed on the pubis rubs against the independent inflatable part, which can cause premature wearing of the walls, potentially resulting in a low-pressure rupture. This is a recurrent problem for ED implants when they are used in the phalloplasty. The angle formed between the FTM penile implant and the pubis, and the presence of the internal support tongue on the inflatable part, which follows the curve of the deflated implant, reduces the risk of folding and breakage (see the figure). View of the deflated ZSI 475 FTM implant “sustained” by the internal tongue The ED penile implant was designed to be placed in the cavernous body attached to the pubic branches located in the legs. The tubes of the ED penile implant rotate forward and toward the scrotum where the pump is located. In the case of phalloplasty, the part between the legs is affixed to the pubis. The tubes emerge upward and away from the intrascrotal pump located below. The tubes must form a downward loop. This encourages premature fatigue in the tubes, which can cause them to break. Exit side of the tubes have been changed to avoid risks of rupture. Also, it is way less noticeable from outside. With the ZSI 475 FTM penile implant, the angle of the tube that connects the inflatable part with the pump is lateral to avoid injuring the urethra. The tube is positioned underneath in order to place the intra–scrotal pump in a natural unobtrusive way. The ED penile implant has a distal part with an ogive (pointed) shape made of dense silicone, which can perforate the phalloplasty during coitus. This small-diameter pointed shape doesn’t come close to emulating a glans or filling out the phalloplasty. The glans of the FTM penile implant allows a proper filling of the tip of the phalloplasty, which reproduces the look and feel of the glans of a cisman. The silicone used is of low density, which reduces the risk of compressing the cutaneous tissue. The glans also provides a good contact surface for the interior of the remnant during coitus, distributing pressure and reducing the risk of perforation. In case of fibrosis in the phalloplasty, the surgeon could have difficulty working the glans, 25mm in width, into its final position. The glans is completely made of silicone, and the surgeon can re-shape it easily. Moreover, this glans is designed to accommodate the urethra. The glans has a flattened covered bottom portion with a groove to accommodate the passage of the urethra and avoid the possibility of pressure zones. The ED penile implant is supposed to be inserted into the corpus cavernosum. Once inflated, its diameter is limited to between 14 mm and 16 mm per cylinder (note that ZSI ED devices have the biggest width on the market). In the majority of FTM cases, the surgeon places only one of the two inflatable implants that comprise the prosthesis; the fill volume is not sufficient, because the ED implant “swims” in the phalloplasty and there is no glans. Placing only one cylinder in the phalloplasty also creates a reliability problem. The surgeon must cut and seal the extra tube attached to the part of the inflatable prosthesis that has been removed. The pressure in the inflatable prosthesis can reach more than 500 mbar, and leaks of hydraulic liquid are common, with which the functionality of the prosthesis quickly begins to fail. Some surgeons place both of the ED implant’s inflatable prostheses in the phalloplasty. The level of “fill” improves, but several issues arise: The body of the penile implant designed for phalloplasty reaches 22 mm in diameter when inflated. Adding to this the fatty tissue and thickness of the skin of the phalloplasty, the total diameter reaches 40 mm. Along with the glans, this diameter provides the appearance of a penis. One of the ED penile implants available on the market has a single thin wall made of a mixture of silicone and plastic. Along with the unnatural noise the wrinkling plastic makes as the phalloplasty moves, there is also a significant risk of perforating the wall of the implant when making abrupt movements. The inflatable part of the FTM penile implant is composed of three layers: an interior cylinder made of silicone, a polyester cylinder, and a silicone cylinder coated with PVP to prevent infections. If a suture needle makes strong contact with the implant, the risk of perforating the interior silicone tube is limited. The polyester tissue used is a quality-tested arterial prosthesis that takes several folds without weakening or tearing. The pump of the ED penile implant, located in the scrotum, is large enough to be found by the patient, and has to be placed in the middle of both testes. This is possible in a cisman morphology because after turning 50, the scrotum gets larger and becomes more flexible. But it is problematic to fit these pumps into neo-scrotums, because they are smaller than a testis prosthesis, but too big to be placed with two testis prostheses. The ZSI FTM pump has been covered with a membrane that is to be filled according to the testis on the other side of the scrotum, to be used as a testis. The diverse complications arising while placing ED penile implants in phalloplasties has allowed us to address their shortcomings and consider how to improve them. Moreover, it has been possible to develop penile implants specifically designed for FTM that address these defects. The ZSI 475 FTM and ZSI 100 FTM penile implants, adapted for phalloplasty, actually solve the problem of fixation to the pubis by giving a “framework” to the phalloplasty. The tubes were correctly “aligned” and the weaknesses were resolved in a positive manner. The FTM penile implants should significantly reduce the rates of failure and revision, as well as the costs associated with replacing unsuitable implants. Even more important, the FTM penile implants improve patient satisfaction and personal development. MTF individuals are women who were assigned male at birth. Many MTF people who suffer from gender dysphoria might decide to do reconstructive surgeries. Construction of the vagina is one of the most sought-after operations. This neovagina is a sort of “tunnel” created amid the rectum, the urethra, and the bladder. The male anatomy has only a small flap of tissue in the perineum to create a vagina. The surgeon creates a space between 12 and 18 cm long behind the bladder, the size depending on the size of the patient. Once this tunnel has been created, the internal walls must be covered with tissue; otherwise, they will close again, as it would occur with any wound. The majority of surgeons use the skin of the penis or of the scrotum for this, as well as the coating of the urethra. If the neovagina is left like this after the operation, it can retract or become necrotic, and at the end of six months it will be closed again. Therefore, the tissues of the neovagina must be applied correctly to the walls of this “tunnel,” to generate new vascularization, which “feeds” the new organ. Until the scarring is complete, the neovagina must be kept open to maintain its amplitude. One manufacturer formerly offered a product made of silicone for this purpose. But the company stopped making it, and surgeons felt compelled to use various “homemade” implants (gloves filled with fabric, for example) that could be formed into more or less acceptable shapes, in order to induce new vascularization and prevent the vagina from closing naturally through scarring. ZSI, inventor and manufacturer of urinary and penile implants, but also FTM devices, understood the need for a new product designed for MTF patients. This “expander” is an oblong silicone ball that fills with air. Thanks to its valve system, the expander can be filled according to the needs and the anatomy of each patient. The ZSI expander facilitates vaginoplasty procedures and assures good scarring of the neovagina walls when the implant is used according to the surgeon’s recommendations. More information on www.zsimplants.chTrans-identity is a reality, and it is a complex subject.
Why ZSI Implants for FTM patients
Surgical teams may be composed of urologists and/or plastic surgeons, it depends.
Profiles of the patient (age, libido, partner etc.) and morphologies, uses and needs are completely different, and this kind of ED devices are not adapted to transmen.IMPLANTS FOR PHALLOPLASTY ZSI 100 FTM AND ZSI 475 FTM
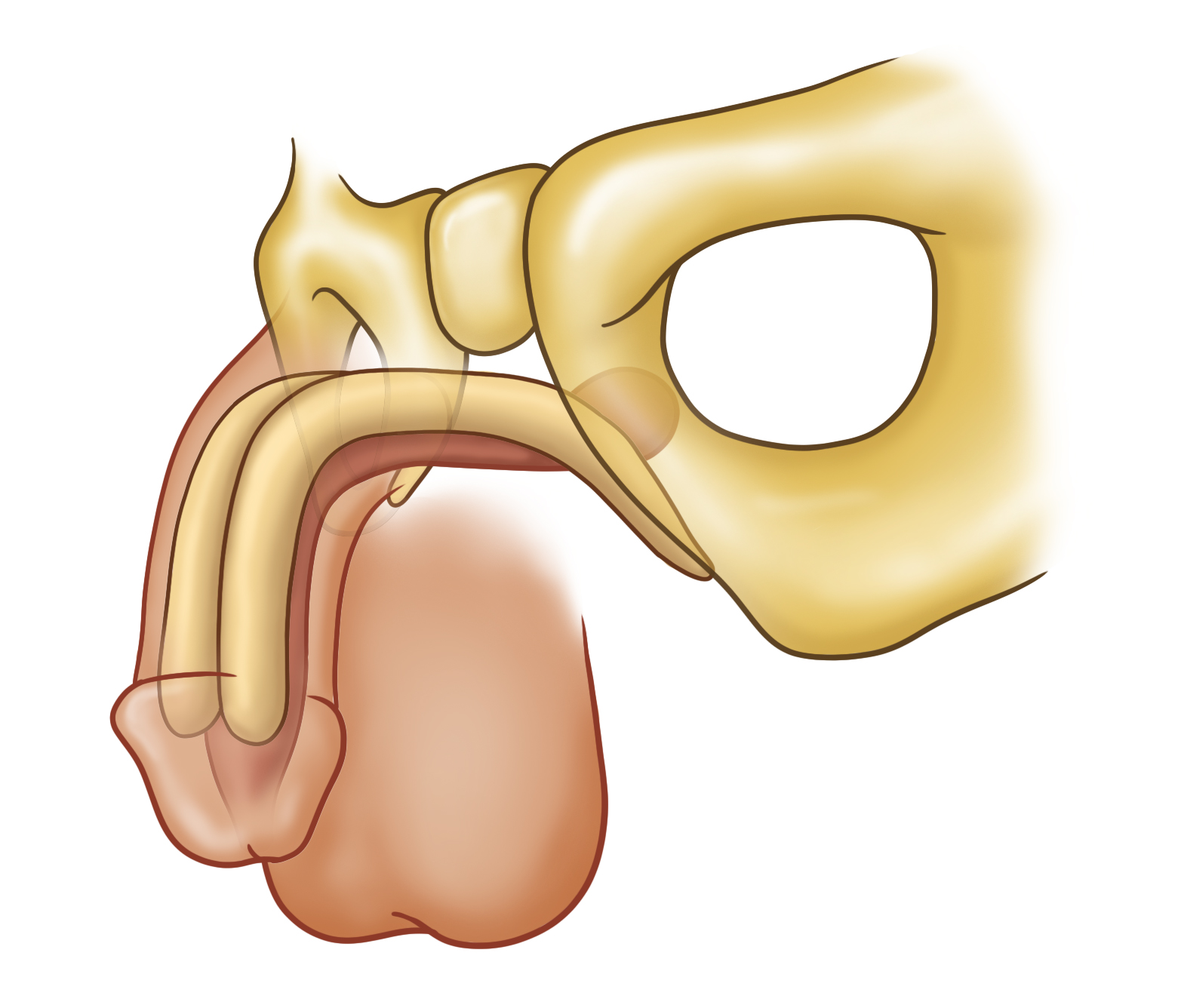
Figure of a penis with corpora cavernosa, spongy tissues, and glans
PENILE IMPLANTS FOR ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
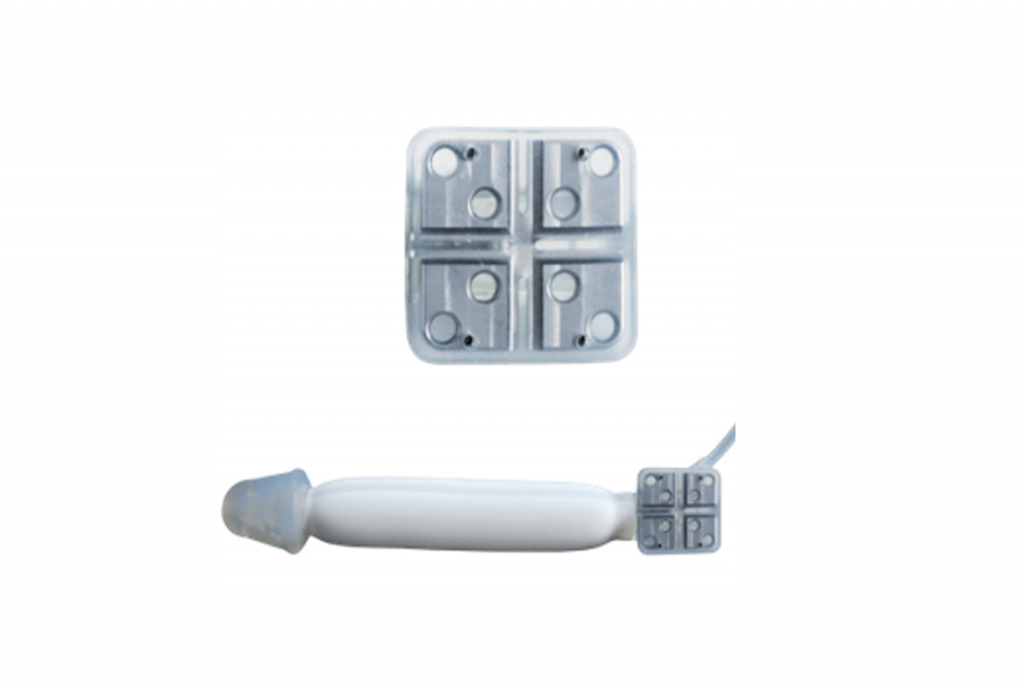
Although well-adapted for erectile dysfunction in the corpora cavernosa, these penile implants are not adapted to the phalloplasty.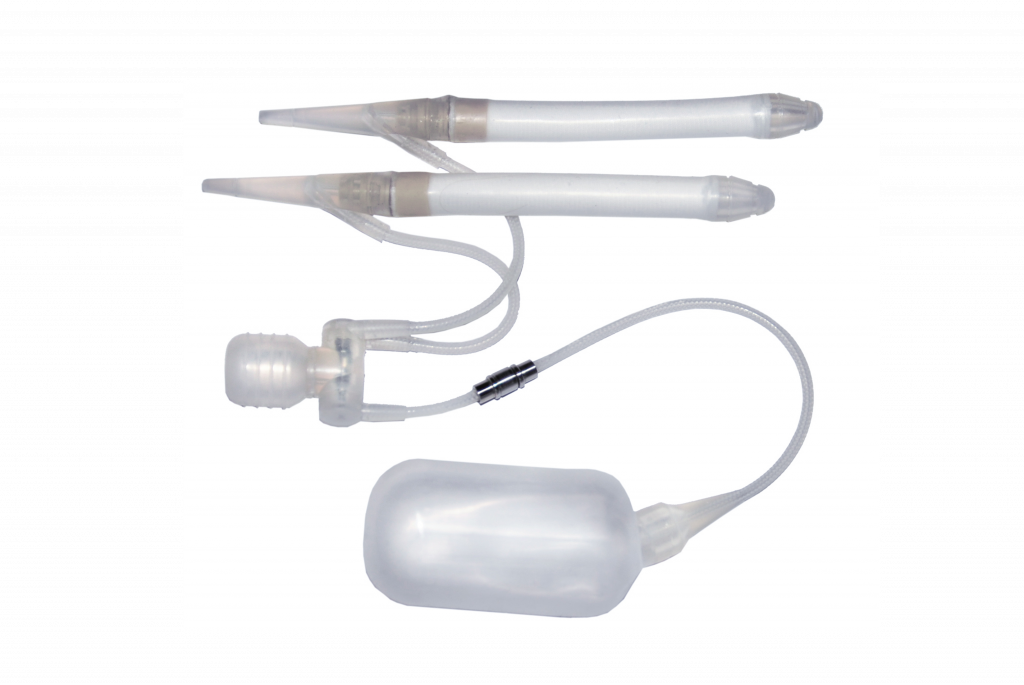
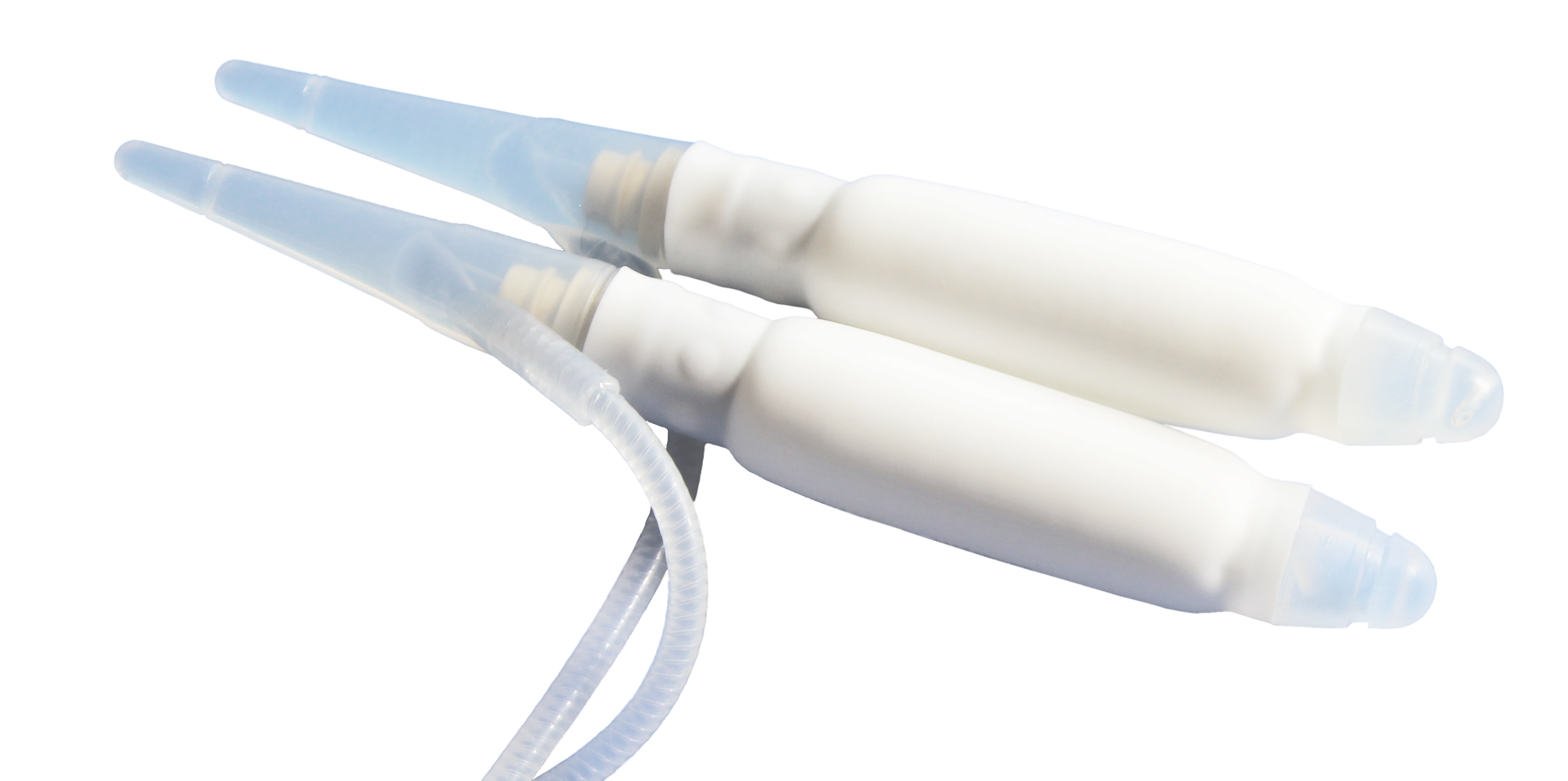
Three-component inflatable implant
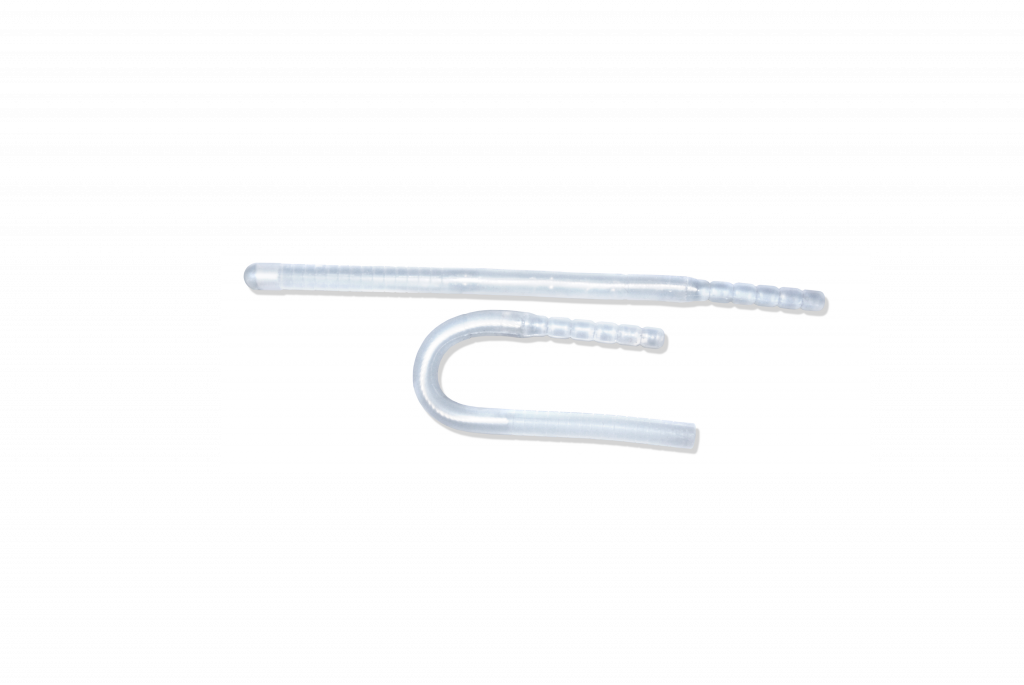

Malleable implant
ZSI FTM IMPLANTS
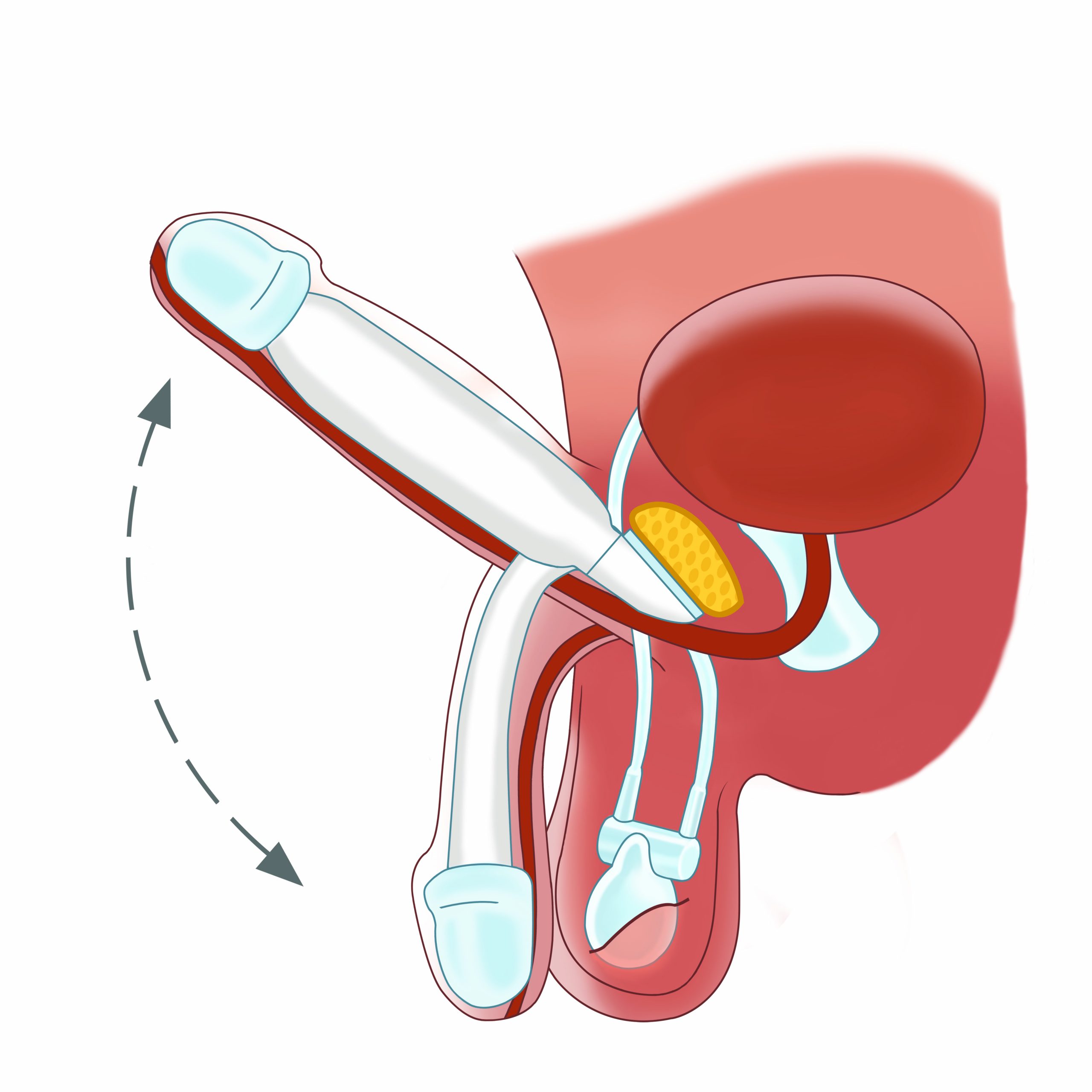
PENILE IMPLANTS FOR FTM ARE ADAPTED
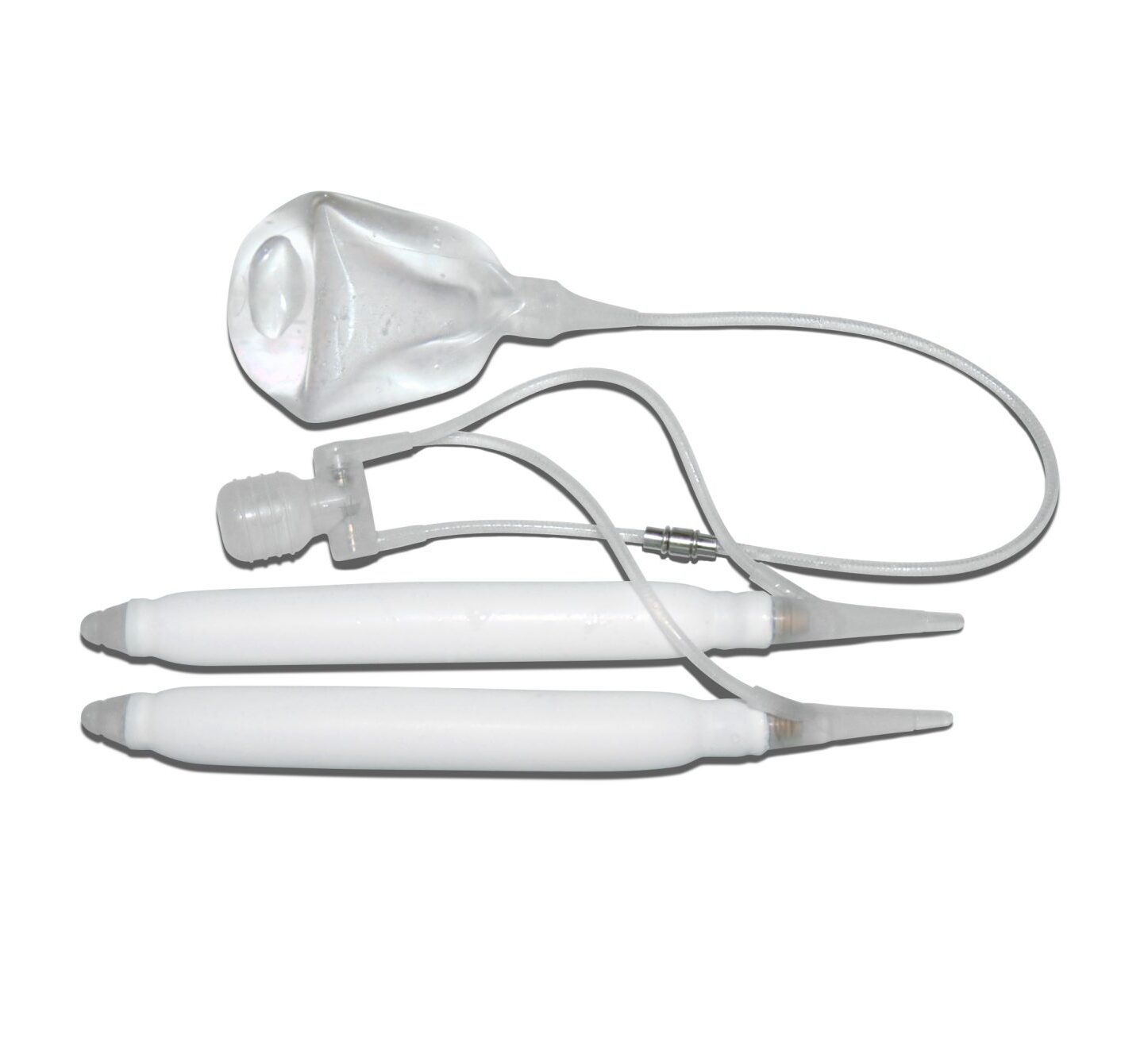

ED implant
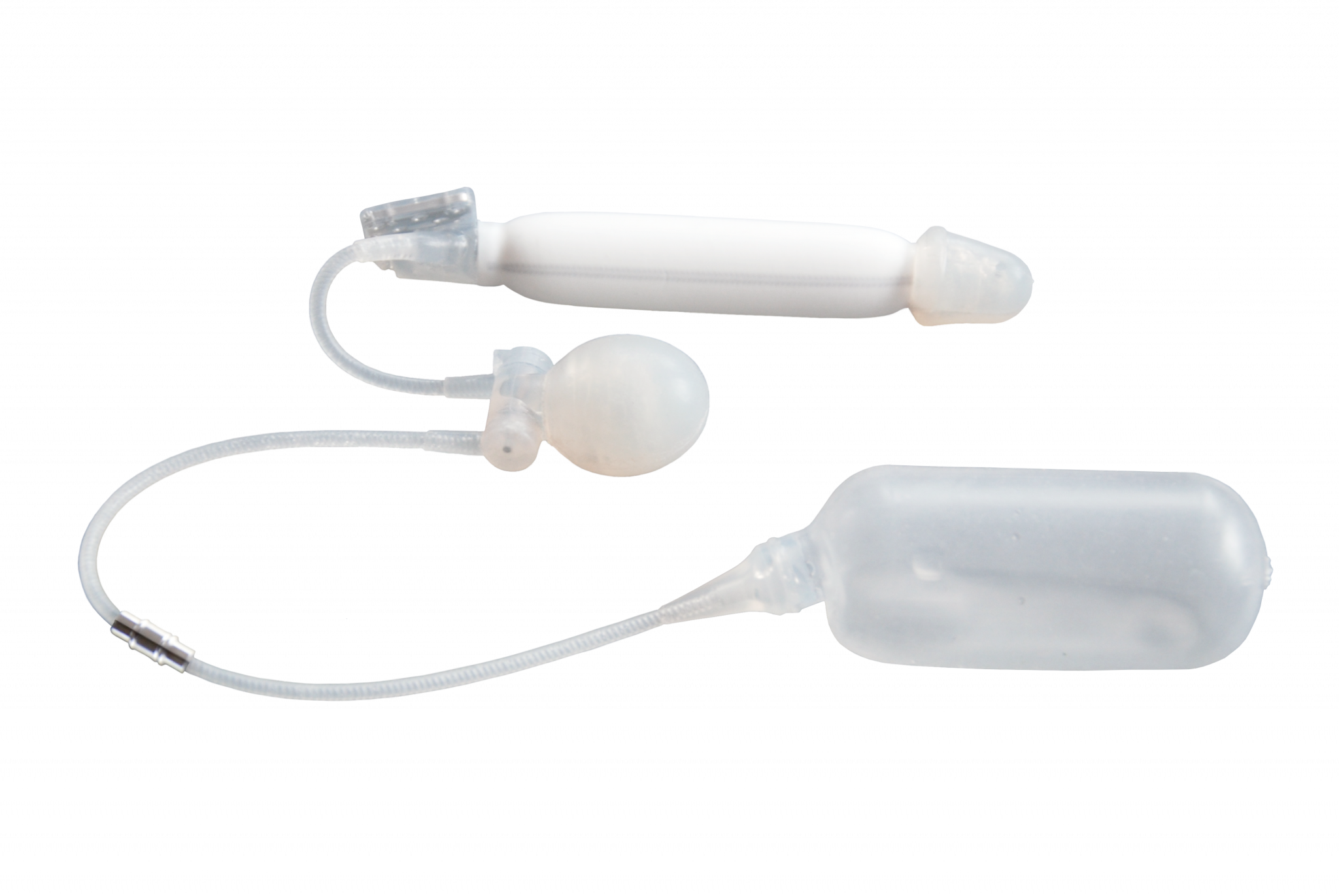
Implant ZSI 475 FTM
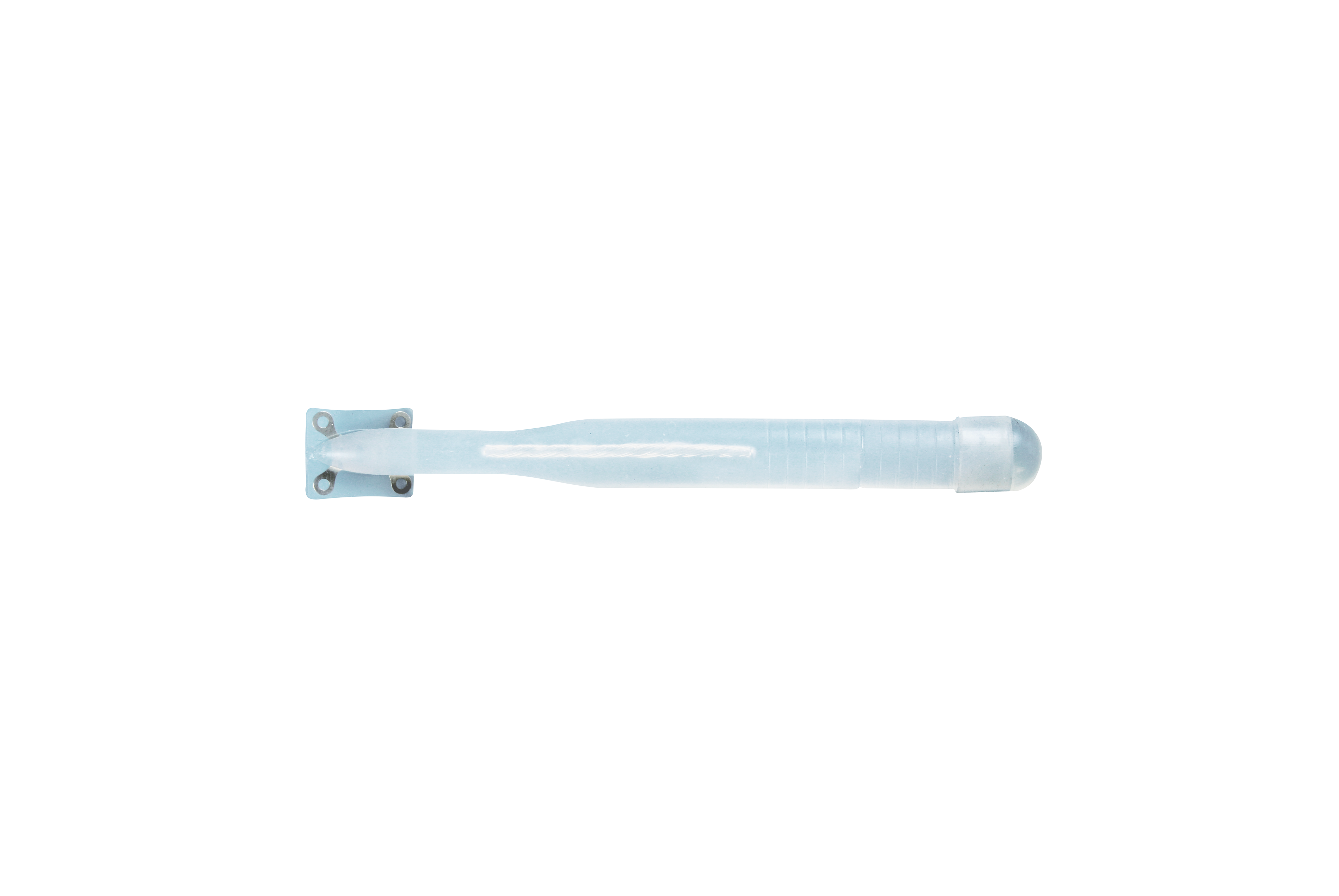

Implant ZSI 100 FTM
FIXING OF THE ZSI 475 FTM AND ZSI 100 FTM IMPLANTS
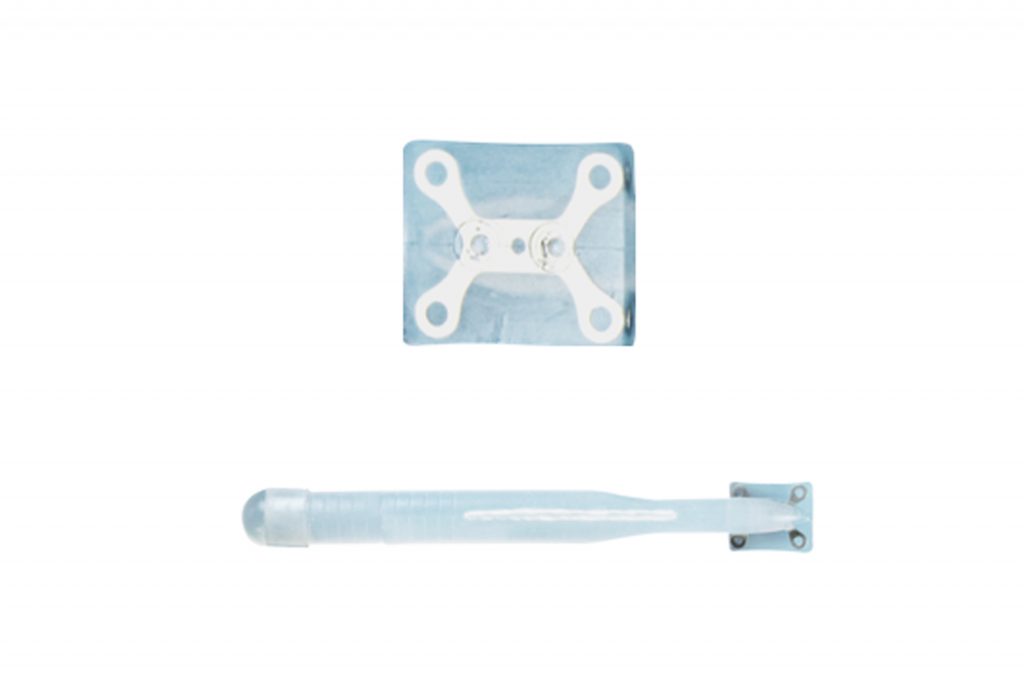


THE ZSI 475 FTM AND ZSI 100 FTM PENILE IMPLANTS HAVE A CALCULATED ANGLE OF ERECTION
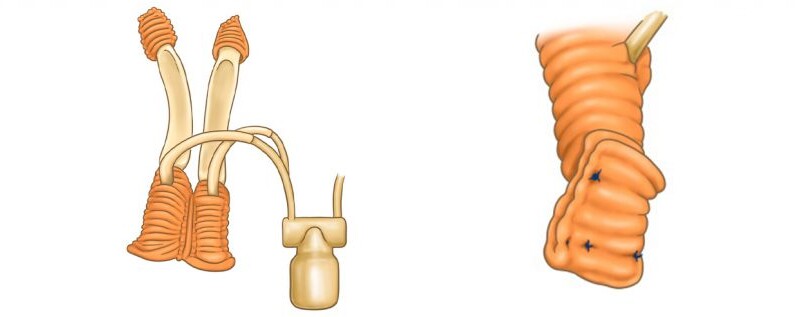
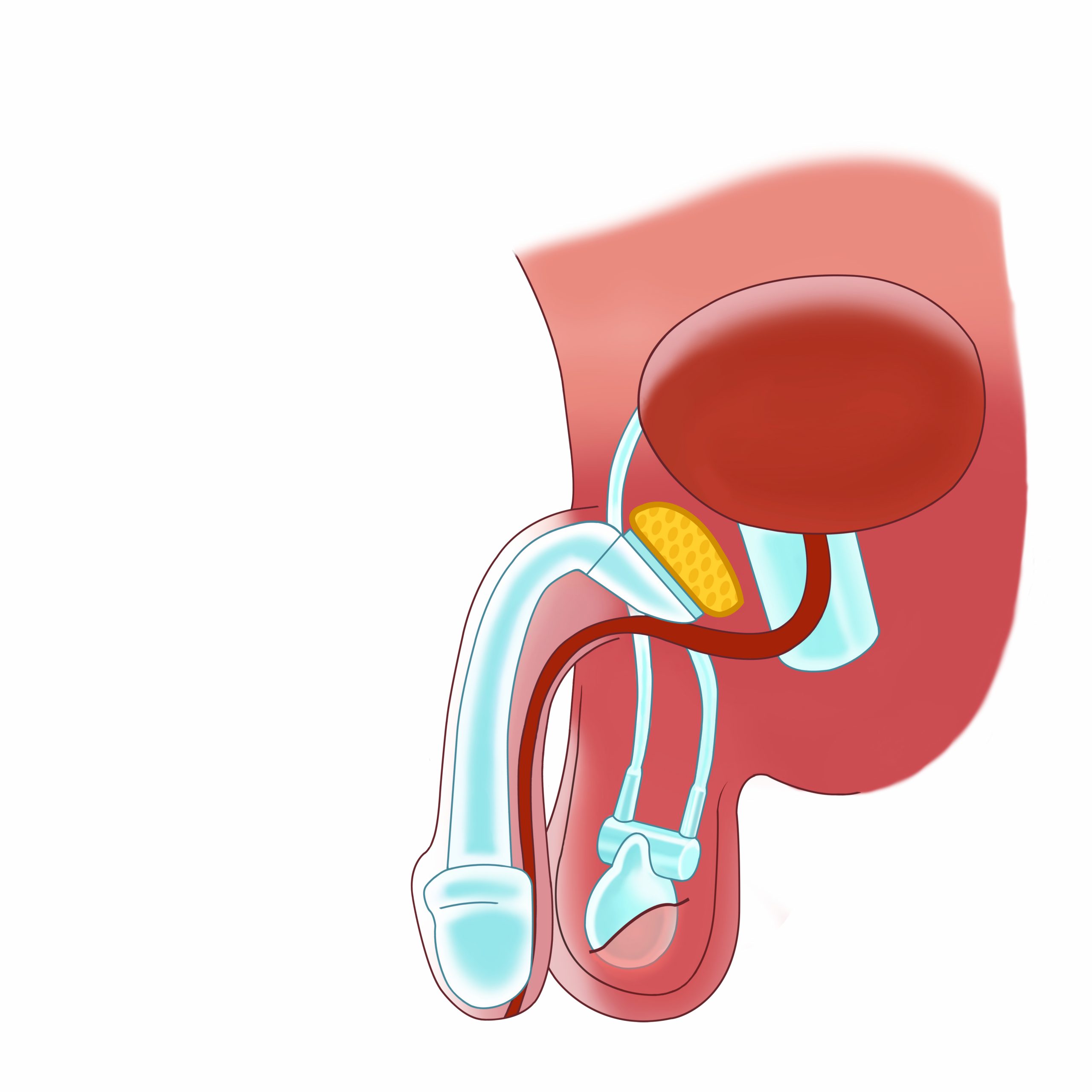
Diagram of the ED implant in erection “fixed” to the symphysis
FTM PENILE IMPLANTS HAVE A TESTED ANGULATION IN DETUMESCENCE

Diagram of the deflated ED implant “fixed” to the symphysis
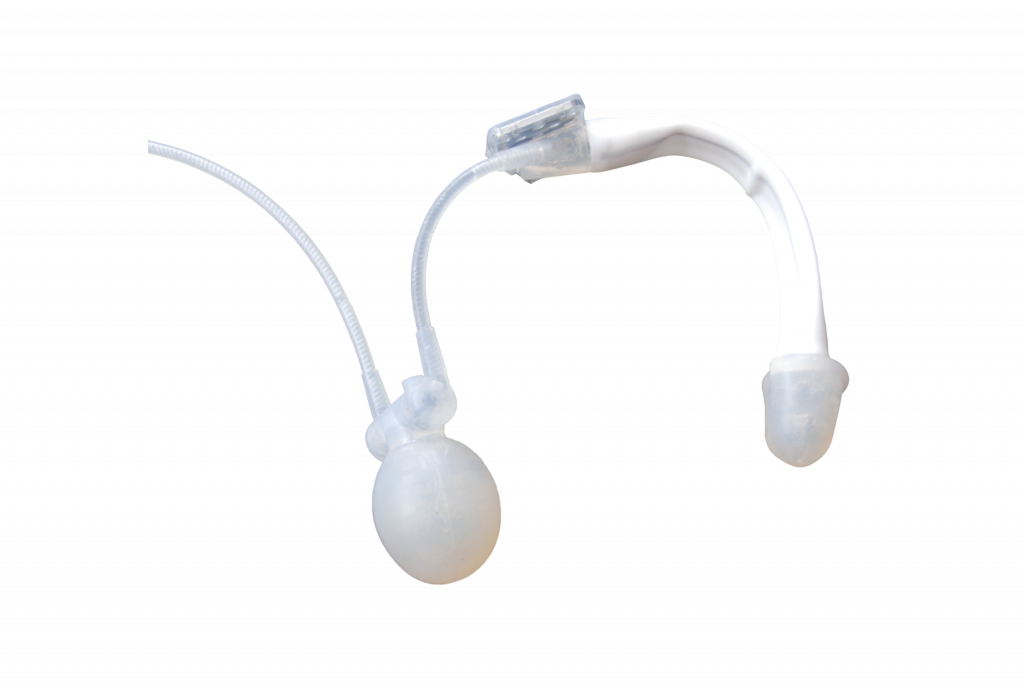
ZSI 475 FTM, junction of inflatable and rigid parts
THE EXIT ANGLE OF THE TUBE OF THE FTM PENILE IMPLANT IS SUFFICIENT FOR PHALLOPLASTY
ED implant showing the exit angle of the tubes toward the front
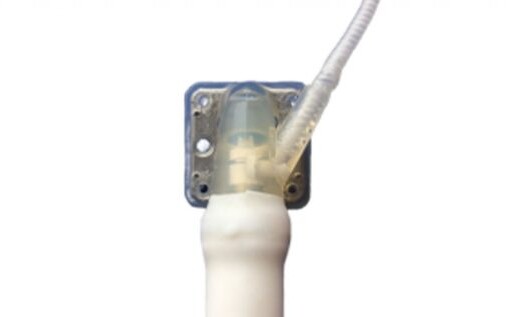
THE GLANS OF THE FTM PENILE IMPLANT

THE BODY OF THE FTM PENILE IMPLANT IS DESIGNED TO “FILL OUT” THE PHALLOPLASTY
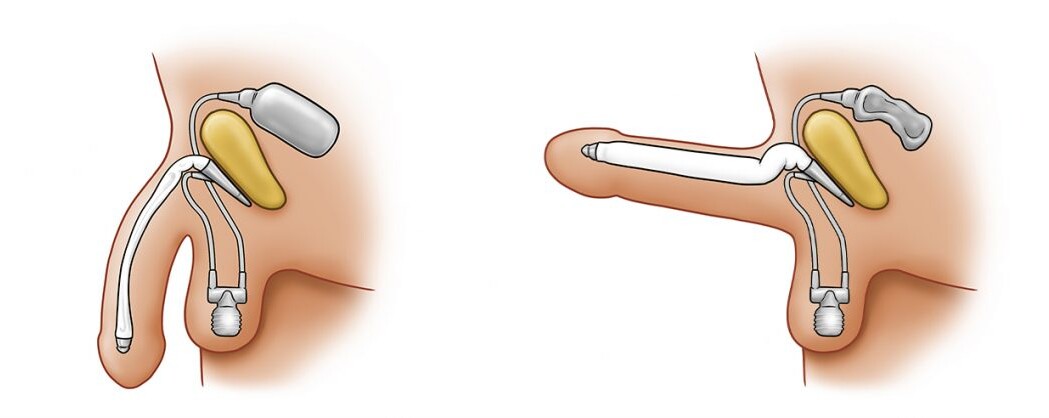
ED penile implant inserted in a phalloplasty
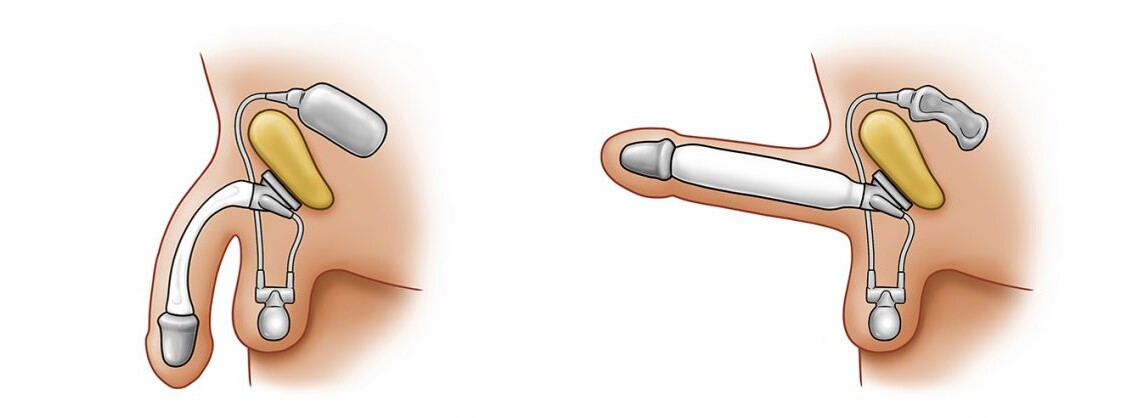
ZSI 475 FTM inflatable implant inserted in a phalloplasty
THE FTM PENILE IMPLANT HAS AN IMPROVED INFLATABLE PART

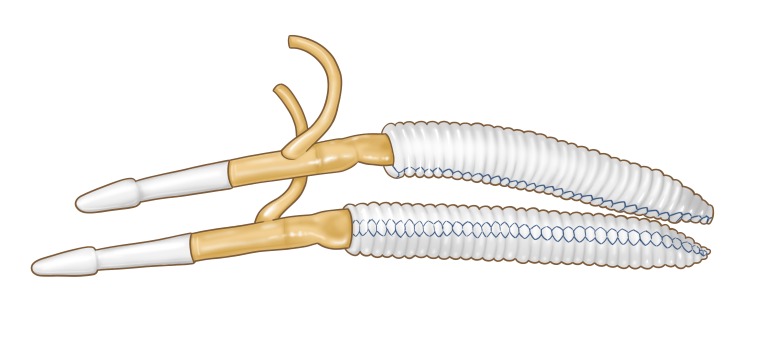
Structure of the inflatable part of the ZSI 475 FTM implant
THE PROBLEM OF PUMP SIZE IN ED PENILE IMPLANTS

Various pumps of ED implants
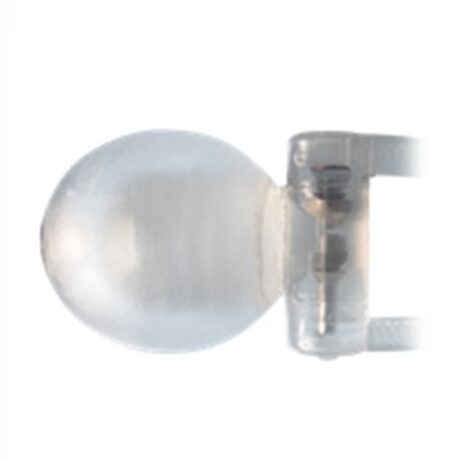

Pump of the ZSI 475 FTM implant surrounded by the membrane
CONCLUSION
Why ZSI Implants for MTF patients
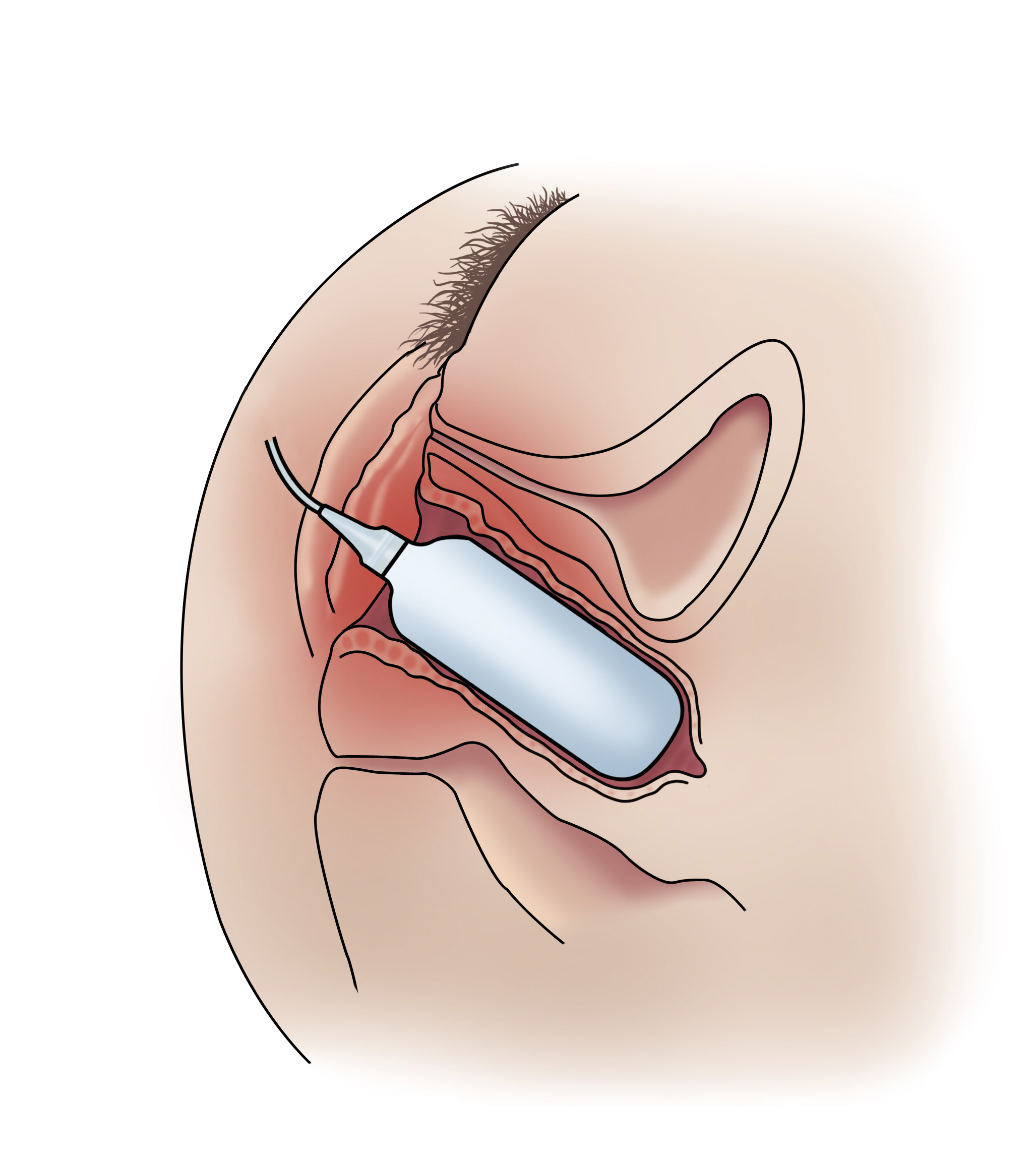
ZSI 200 NS Expander
There is a video to understand better the process of Vaginoplasty surgery.